
Absorbance vs wavelength for S1, S2, S3 and S4. Inset is for pure ZnS... Download Scientific
The act or process of absorbing or the condition of being absorbed. Oct 19, 2021 Absorbance (physics) A logarithmic measure of the amount of light that is absorbed when passing through a substance; the capacity of a substance to absorb light of a given wavelength; optical density. Oct 19, 2021 Absorption A state of mental concentration.

Sensory Perception · Anatomy and Physiology
This page titled 13.1: Transmittance and Absorbance is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by David Harvey. As light passes through a sample, its power decreases as some of it is absorbed. This attenuation of radiation is described quantitatively by two separate, but related terms: transmittance and..

Adsorption vs Absorption Differences and Examples
Answer While absorption is the process of energy transfer of light into a medium that it passes through, absorbance is a quantification of exactly how much light is absorbed by the medium. Additional resources Absorption Spectrum Viewer What is the difference between absorbance and absorption?

Normalized absorbance and emission intensity spectra versus wavelength... Download Scientific
Absorbance (A) is states how much of the light the sample absorbed. while absorptance is absorbed radiation and incident radiation in a ratio format Cite 1 Recommendation Thomas Mayerhöfer.
Decoding Your Absorbance Readings Vernier
The result is an absorbance spectrum that shows the intensity of emission as a function of wavelength. As is the case for emission spectra, absorbance spectra range from narrow lines to broad bands. The atomic absorption spectrum for Na is shown in Figure 6.4.4 6.4. 4, and is typical of that found for most atoms.
Beer Lambert Law Transmittance & Absorbance Edinburgh Instruments
The absorbance is directly proportional to the concentration (\(c\)) of the solution of the sample used in the experiment. The absorbance is directly proportional to the length of the light path (\(l\)), which is equal to the width of the cuvette. Assumption one relates the absorbance to concentration and can be expressed as \[A \propto c.
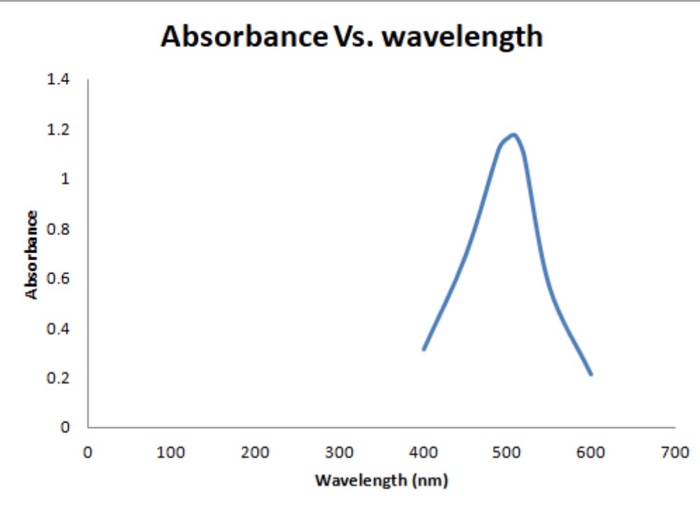
Solved Absorbance Vs. wavelength Absorbance 0 100 200 500
Absorbance vs. Transmittance. The absorbance value can range from 0 to infinity, where a higher value indicates a greater absorption of light. Absorbance is commonly used to quantify the concentration of a substance in a solution, as it follows Beer-Lambert's Law, which states that absorbance is directly proportional to the concentration and.

Absorption spectrum (absorbance vs wavelength) of rutin obtained at the... Download Scientific
Absorbance refers to the amount of light absorbed by a substance, while absorption is the process by which a substance takes in another substance or energy. Absorbance is measured using a spectrophotometer, which measures the amount of light absorbed by a substance.
PPT Absorbance spectroscopy PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3102589
As nouns the difference between absorption and absorbance is that absorption is the act or process of absorbing or of being absorbed as while absorbance is a logarithmic measure of the amount of light that is absorbed when passing through a substance; the capacity of a substance to absorb light of a given wavelength; optical density.

Absorption spectroscopy of haemoglobin species Deranged Physiology
The main difference between them is that adsorption is the adhesion of particles onto a substance, while absorption involves mass transfer into another material. But, adsorption and absorption involve other differences as well. Here is a comparison of adsorption and absorption, a closer look at their definitions, and examples of each process.

Absorbance vs. wavelength graph. Download Scientific Diagram
Absorption spectroscopy is spectroscopy that involves techniques that measure the absorption of electromagnetic radiation, as a function of frequency or wavelength, due to its interaction with a sample. The sample absorbs energy, i.e., photons, from the radiating field. The intensity of the absorption varies as a function of frequency, and this.

(a) Absorbance vs. Wavelength spectrum and (b) Dependence of absorption... Download Scientific
Absorbance is defined as follows: A = -logT For most applications, absorbance values are used since the relationship between absorbance and both concentration and path length is normally linear (as per the Beer Lambert law, described in section 1.9). 1.5 Summary - UV and visible light are part of the electromagnetic spectrum

a Absorbance versus wavelength plots of the aqueous solution 4NP and... Download Scientific
What's the difference between Absorption and Adsorption? Absorption is the process in which a fluid is dissolved by a liquid or a solid (absorbent). Adsorption is the process in which atoms, ions or molecules from a substance (it could be gas, liquid or dissolved solid) adhere to a surface of the adsorbent. Ads.
shows the transmission and absorption spectra of the prepared silicon... Download Scientific
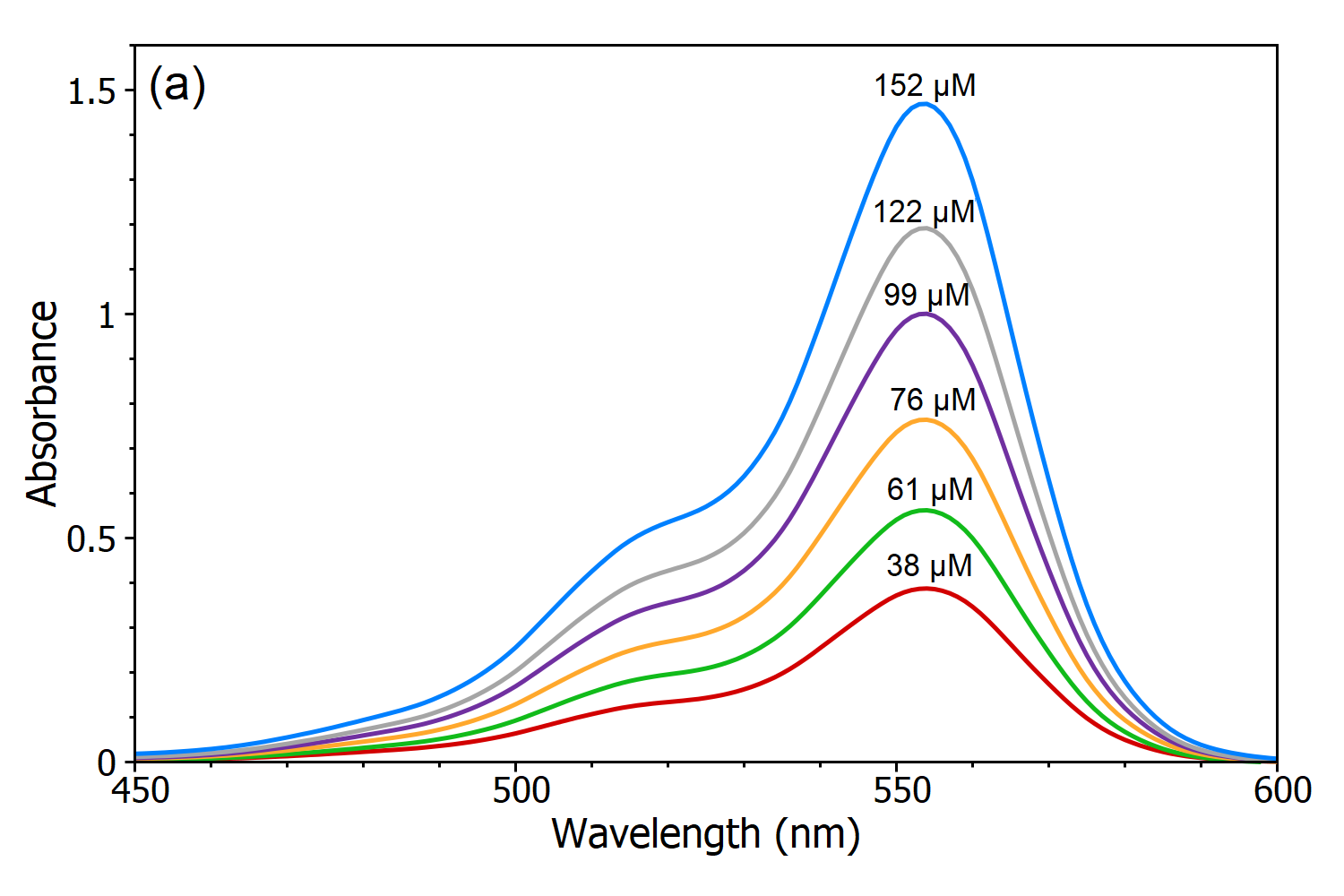
Solutions Absorbance vs Concentration Absorbance vs Concentration Introduction According to Beer's Law, A = εLc, a substance's concentration and absorbance are directly proportional under ideal conditions: a high-concentration solution absorbs more light. In comparison, a low-concentration solution absorbs less light.

Absorption Vs Adsorption The Engineering Concepts
The term absorption refers to the physical process of absorbing light, while absorbance does not always measure only absorption; it may measure attenuation (of transmitted radiant power) caused by absorption, as well as reflection, scattering, and other physical processes.

UVvisible absorption spectra of absorbance versus wavelength during... Download Scientific
You will be applying Beer's law to calculate the concentration. The equation for Beer's law is: A = εmCl. (A=absorbance, εm = molar extinction coefficient, C = concentration, l=path length of 1 cm) You should have a data set which was used to create a standard curve. The graph should plot concentration (independent variable) on the x-axis and.